Materials Design Releases MedeA 3.12 —Train.Deploy.Discover
- Katherine Hollingsworth

- Dec 22, 2025
- 6 min read
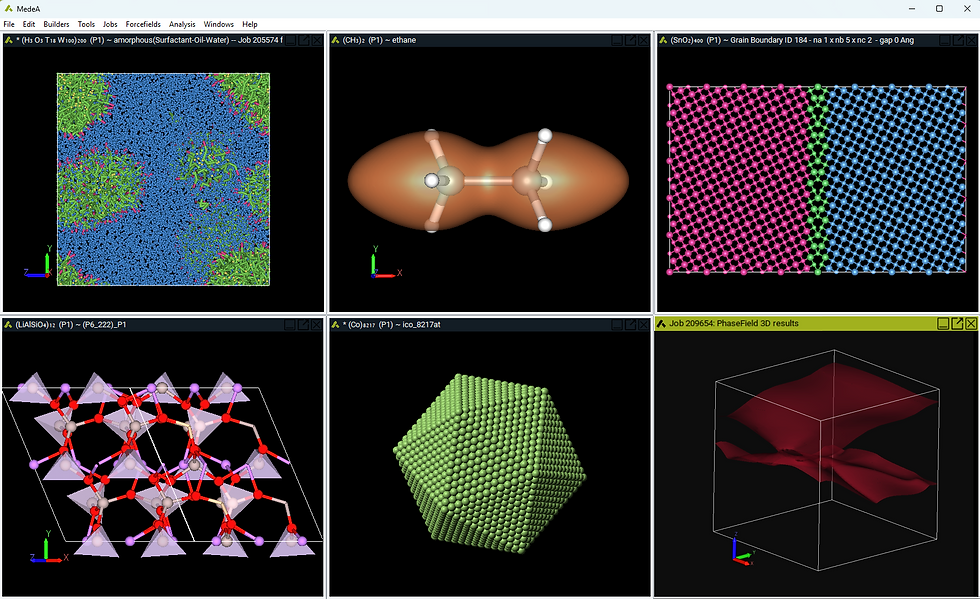
MedeA 3.12 —Train.Deploy.Discover
Materials Design announces MedeA 3.12, materials simulation environment, delivering a revolutionary integration of machine learning capabilities that transform materials modeling workflows. The MedeA 3.12 release establishes a comprehensive machine-learned potential ecosystem spanning training, refinement, deployment, and analysis, while introducing powerful new builders for complex microstructures and enhanced tools for materials discovery.
Key Features of MedeA 3.12
Complete MLP Workflow Integration: Seamless pipeline from VASP MLFF training to LAMMPS deployment with automatic .frc file generation
Foundational Model Support: GRACE-1L-OMAT, GRACE-2L-OMAT, GRACE-1L-OAM and GRACE-2L-OAM universal machine-learned potentials available for immediate use in LAMMPS
MLPG Enhancements: Direct fitting of GRACE potentials (1L/2L) within the MLPG module for custom forcefield development
Advanced MLFF Capabilities: Descriptor reduction, spilling factor quality assessment, and enhanced training set management in VASP
Perturbation Builder: Systematic generation of diverse training sets with controlled perturbations of lattice parameters, positions, and magnetic moments
High-symmetry Grain Boundary Builder: Comprehensive CSL database for nine crystal lattice types enabling systematic interface studies
Enhanced Analysis Tools: New Similarity Analysis for intelligent structure selection from large MLP training datasets
Temperature-dependent P3C: Advanced polymer property predictions with PEARL library exceeding 3 million repeat units
Dr. Clive Freeman, CEO of Materials Design comments:
"The MedeA 3.12 environment delivers a complete machine learning workflow for materials modeling. Researchers can now generate training sets with the Perturbation Builder, develop MLFFs in VASP with quality assessment tools, and seamlessly deploy those forcefields in LAMMPS for large-scale simulations. The foundational GRACE models provide immediate access to universal potentials, while MLPG enables custom forcefield fitting. Combined with the new high-symmetry grain boundary builder and Similarity Analysis tool for managing large datasets, this release provides practical solutions for the full spectrum of materials discovery challenges. We’re excited to see how these integrated capabilities accelerate research workflows across the community."
Description of MedeA 3.12
New Features and Enhancements
MedeA 3.12 December 2025
An overview of updates in this MedeA release is provided below.
Builders and Editors and Visualization
Microstructure Builder
Insertion of interstitial atoms at grain boundaries
Easy creation of multiple slab structures
Rotations can be specified as hkl indices
Custom supercell builder: a warning is issued if the resulting supercell is left-handed (the system is still built)
Interface Builder
High-symmetry grain boundary builder (NEW)
A database of Coincidence-Site-Lattice (CSL) grain boundary models for both twist and tilt types, with Σvalues up to Σ13, is included. The following crystal lattice types are supported
face-centered cubic (fcc),
body-centered cubic (bcc),
hexagonal close-packed (hcp),
simple cubic (sc),
rocksalt,
zincblende,
wurtzite,
nickeline, and
fluorite
Models can be customized by specifying size, lattice parameter, and atom types (elements)
Multiple grain boundary models can be built simultaneously and saved in a structure list
The builder is accessible both as an interactive tool and as a flowchart stage

Perturbation Builder (NEW)
Particularly useful for creating training sets for forcefield fitting and machine learning
Lattice parameters (cell lengths and angles) can be randomly perturbed
Magnetic moments for all or selected atoms can be set
Atomic positions (x, y, z) can be randomly perturbed
Magnetic moments can be randomly perturbed
The builder is available as an interactive tool and as a flowchart stage
Amorphous Materials Builder
Enhancements for the detection of molecules with large cycles
Engines
VASP
New binaries (VASP 6.5.1) are provided with additional features
Export of machine-learned forcefields (MLFF) as .frc files which can be used in MedeA LAMMPS simulations
Support for data exchange via HDF5 files
Support for exchange-correlation functionals from the libXC portable library of functionals at libxc.gitlab.io (DFT, metaGGA, and hybrid functionals)
Support for DFT-D4 van-der-Waals interactions
Access to the library for Many-Body Dispersion interactions provided by libMBD
MLFF enhancements
Controls to reduce the complexity of atomic environment information for increased efficiency have been added: element-reduced three-body descriptors and angular descriptors
Quality assessment is now provided using the spilling factor, both in applications and during on-the-fly training
Use of structure lists for the entire training set now makes this independent of trajectory file frequency settings
Enhanced help text for MLFF options with keyword links
Flowchart enhancements:
Ability for a VASP flowchart stage to access files from previous stages and/or jobs, enabling improved access to:
Wave functions and charge densities for restart
Final configuration and velocities for MD continuation
Trainings sets for continued on-the-fly training or refit
Machine-learned forcefields for application
Core-level energies are now computed and reported in the ListOfResults.sli structure list
A system-independent non-default user choice of the number of bands has been implemented
Improved performance by offering greater flexibility for ScaLAPACK
Integrated DOS data and related parameters has been added to DOS data for use in the training of machine-learned potentials
Enhanced autocorrection procedures to allow user intervention
Submission of left-handed systems is prevented with informative warnings
PhaseField
Temperature evolution over time is computed as a function of heat capacity and thermal conductivity
Temperature dependencies of material properties (bulk/grain boundary diffusion, free energy, eigenstrain) are supported
Boundary conditions and initial temperature scenarios can be defined
Visualization of 3D PhaseField results is enabled in Analysis
LAMMPS
New binaries (Jul2025) are provided
Machine-learned potentials (MLPs) created by VASP on-the-fly training (MLFF) are supported
ACE & GRACE (1L/2L) machine-learned potentials are supported
Stress uncertainty evaluation for non-standard orientations is enhanced
On-the-fly computation of angle and dihedral distributions
On-the-fly computation of the radius of gyration of molecules
GIBBS
Enhancement for sorption simulations on systems with very large solids (unit cell replicated multiple times in each direction); output structures include only the sorbed species
Forcefields
MLPs
GRACE 1L and 2L MLPs are supported in LAMMPS
VASP-generated MLPs (MLFF) can be used in VASP and/or LAMMPS
Foundational (universal) machine-learned potentials GRACE-1L-OMAT, GRACE-2L-OMAT, GRACE-1L-OAM and GRACE-2L-OAM are available for use with LAMMPS
MLPG
Fitting GRACE potentials (1L/2L) is enabled within the MLPG module
PCFF+
New parameters for boric acid, borate and silicate ions, with refined treatment of fused-ring aliphatics
Property Modules
P3C
Temperature-dependent property calculations have been added to the Flowchart P3C stage; graphs for computed temperature dependencies are generated automatically
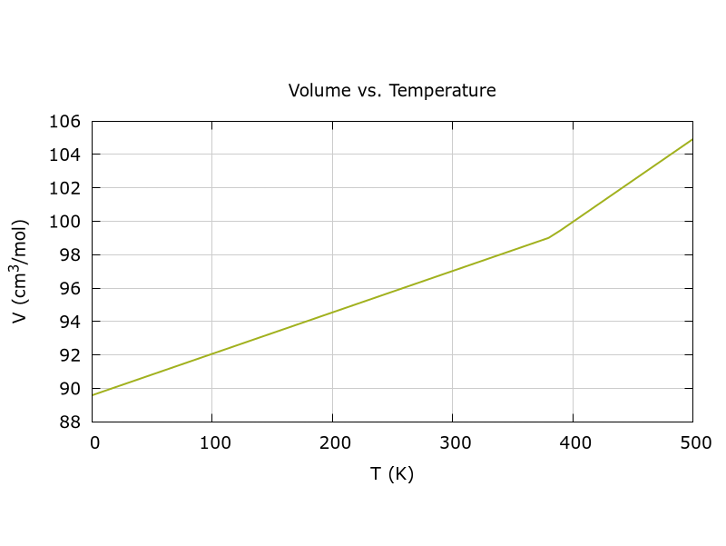
Copolymer property enhancements
Properties are reported as described in Chapter 18 of Prediction of Polymer Properties (Jozef Bicerano): Tg, Td12, aT, Density, cp, solubility1, g1, Ref, diel, vpoisson298K, B298K, Eyoung298K Gshear298K,Bf298K, Sy298K, Eavis, PO2, PCO2, and Tc
Specific heat capacity (cp) is now reported for copolymers
Updates for g1, Eyoung298K, Gshear298K, vpoisson298K, V, B298K, Bf298K improve agreement with reference data
Td12 and EyoungTgp30K calculations have been improved
Documentation updates
Reporting of temperature-dependent properties
Copolymer property enhancements
Quality of statistical fits is described
Tabulated flowchart variables for properties and descriptors
Polymer Expert
The PEARL (Polymer Expert Analog Repeat unit Library) now includes more than 3 million repeat units. Latest version: 2025-07-28
UNCLE
Optimization stage
The ability to resume cluster expansion optimizations from a previous stage, job, or UNCLE structure list has been added

Reference energies for all elements in the model are now calculated automatically, ensuring accurate heats of formation for all enumerated structures

Analysis
Binary Ground State Diagram Analysis (UNCLE)
A control for switching the y-axis between “Total energy,” “Pseudo heats of formation,” and “Heats of formation” has been added
Support for plotting data from the Calculate Property Stage with color-coded properties has been added
The random mixing energy curve is plotted when available
High-resolution screen support has been improved
Monte Carlo Temperature Profiles
Support for high-resolution screens has been improved
Band Structures and Phonon Dispersions Plot
A Style panel has been introduced, allowing customization of color, scale, and size of measuring lines, Fermi line, and axes. The plotting range and axis placement can be fine-tuned, and the background color can be changed. Styles can be reset, saved, or loaded
Support for high-resolution screens has been improved


Similarity Analysis (NEW)
Structural similarity in lists (sli, fts, trj) can be checked
Smaller subsets including representative structures can be generated
Implemented as an interactive builder and as a flowchart stage

Radius of Gyration (NEW)
Computation of the radius of gyration for selected molecules from an MD trajectory or a structure list
Implemented as an interactive builder and as a flowchart stage
Geometrical distributions (NEW)
Computation of distances, angles and torsions for selected subsets of atoms (single, pair, triplets)
Implemented as an interactive builder and as a flowchart stage
Constitutional descriptors’ list updated to consist of Joback & P3C descriptors
JobServer & TaskServer
TaskServer SLURM Wrapper Script: Monitoring capabilities have been introduced to track the state of submitted tasks in the SLURM queue, ensuring smooth execution
Enhancements for transfer of large files to the JobServer
#machinelearning #modeling #materialscience #VASP #LAMMPS #GIBBS #UNCLE #softwarerelease #compchem #flowcharts #machinelearning #VASP6 #MLP #GPU #Computeengines #Propertymodules #mesoscale #timescale #forcefield #batteries #energy #automotive #MedeA #semiconductors #python #P3C #polymers #PCFF #MLPG #GAUSSIAN #MOPAC #ReaxFF #Amorphous #Quantumengine #MedeA #MedeASoftware #forcefields #ICSD #polymerbuilder #thermosets #amorphous #microstructure #multiscale #databases #MLFF #GPU #Phasefield #Polymerexpert #docking #GRACE



Comments